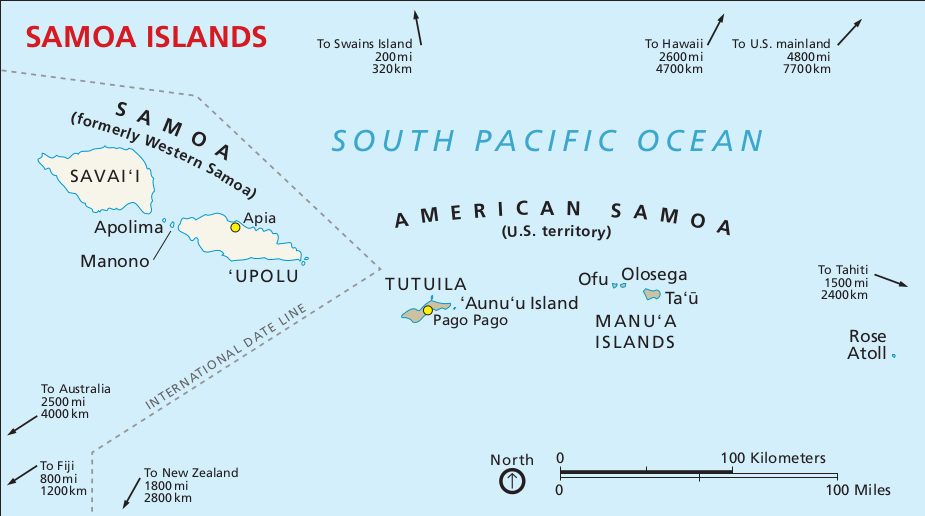
Samoa comprises of two main regions – the independent state of Samoa, formerly known as Western Samoa, and American Samoa. In 1997, Western Samoa dropped the “Western” from its name. The archipelago consists of ten mostly volcanic islands, with Upolu and Savaii being the largest, covering a combined land area of approximately 2,900 square kilometres. In 2021, the estimated population reached 218,764, with many people living on the coastal plains, although some maintain family gardens in elevated areas.
Samoa, known officially as the Independent State of Samoa, consists of four main inhabited islands – Upolu, Savaii, Manono, and Apolima – along with several smaller islets. The capital and largest city of Samoa is Apia, located on the island of Upolu. In contrast, Tutuila serves as the capital of American Samoa, which is an incorporated territory of the United States. Manu’a islands are located 100 kilometres east of Tutuila and are also part of American Samoa.
Samoa has a rich cultural heritage, with a history dating back thousands of years. The Samoan culture is known for its strong sense of community, traditional customs, and deep respect for the environment. The Fa’a Samoa, which translates to “the Samoan way,” encompasses the customs, values, and social structure of the Samoan people.
The islands of Samoa are known for their stunning natural beauty, with lush rainforests, pristine beaches, and crystal-clear waters. The landscape is dominated by volcanic mountains, with Mount Silisili on Savaii being the highest peak. Samoa is also home to many unique plant and animal species, including several endemic species found nowhere else on Earth.

The economy of Samoa is primarily based on agriculture, with copra (dried coconut meat), cocoa, and taro being major exports. Tourism is also an important industry, with visitors drawn to Samoa’s natural beauty, rich cultural heritage, and warm hospitality of the Samoan people.
One notable aspect of Samoa’s history is its unique system of village governance known as the “matai” system. The matai, or chiefs, hold significant authority and play a crucial role in the decision-making process of the village communities.
In terms of governance, Samoa is a parliamentary democracy, with a head of state, known as the O le Ao o le Malo, and a Prime Minister. English and Samoan are the official languages, with Samoan being widely spoken across the islands.
Overall, Samoa is a fascinating and culturally-rich nation with a unique blend of traditional customs and modern influences. Its natural beauty, warm people, and vibrant culture make it a truly special destination for visitors and a cherished home for its people.